JAKARTA (February 18, 2021) - The Director of Social Rehabilitation for Persons with Disabilities in the Ministry of Social Affairs, Eva Rahmi Kasim, explained the importance of collecting data on Persons with Disabilities in a virtual Technical Guidance (Bimtek) on the Social Welfare Information System (SIKS) of Social Welfare Institutions (LKS) for Persons with Disabilities, which was attended by more than 1000 participants throughout Indonesia.
Law Number 11 of 2009 concerning Social Welfare states that LKS are social organizations or social associations that carry out the implementation of social welfare formed by the community, both legal entities and non-legal entities.
LKS is an implementing partner for government programs and as a source and potential for social welfare. "In order for LKS to become one of the parties that can participate in carrying out data collection for Persons with Disabilities, LKS must follow the LKS registration process flow mechanism through the SIKS LKS application developed by the Data and Information Center (Pusdatin) of Ministry of Social Affairs," explained Eva.
"Persons with disabilities are a marginal group, therefore it is important to collect data as a basis for policy making as mandated in Government Regulation Number 70 of 2019 concerning Planning, Implementation, and Evaluation of Respecting, Protecting and Fulfilling the Rights of Persons with Disabilities," Eva continued in her direction.
The Ministry of Social Affairs has currently developed SIKS LKS for Persons with Disabilities which is integrated with the Integrated Social Welfare Data (DTKS). Data collection, which so far has only been household-based, is now expanded to be based on LKS as the organizer of social welfare.
Furthermore, Eva also said that the Disability Center as the Technical Implementation Unit of the Ministry of Social Affairs not only functions as a service but also a place of reference, providing information and communication as well as data collection functions. The Ministry of Social Affairs' Pusdatin is currently also developing a registration application via an Android cellphone so that a person or individual can register for social welfare programs that will be directly connected to the nearest LKS. The LKS then follows up by verifying and validating the incoming data.
"The Ministry of Social Affairs through 19 Disability Centers will carry out one-stop One Stop Services similar to Centerlink," said Eva.
Law Number 11 of 2009 concerning Social Welfare states that LKS are social organizations or social associations that carry out the implementation of social welfare formed by the community, both legal entities and non-legal entities.
LKS is an implementing partner for government programs and as a source and potential for social welfare. "In order for LKS to become one of the parties that can participate in carrying out data collection for Persons with Disabilities, LKS must follow the LKS registration process flow mechanism through the SIKS LKS application developed by the Data and Information Center (Pusdatin) of Ministry of Social Affairs," explained Eva.
"Persons with disabilities are a marginal group, therefore it is important to collect data as a basis for policy making as mandated in Government Regulation Number 70 of 2019 concerning Planning, Implementation, and Evaluation of Respecting, Protecting and Fulfilling the Rights of Persons with Disabilities," Eva continued in her direction.
The Ministry of Social Affairs has currently developed SIKS LKS for Persons with Disabilities which is integrated with the Integrated Social Welfare Data (DTKS). Data collection, which so far has only been household-based, is now expanded to be based on LKS as the organizer of social welfare.
Furthermore, Eva also said that the Disability Center as the Technical Implementation Unit of the Ministry of Social Affairs not only functions as a service but also a place of reference, providing information and communication as well as data collection functions. The Ministry of Social Affairs' Pusdatin is currently also developing a registration application via an Android cellphone so that a person or individual can register for social welfare programs that will be directly connected to the nearest LKS. The LKS then follows up by verifying and validating the incoming data.
"The Ministry of Social Affairs through 19 Disability Centers will carry out one-stop One Stop Services similar to Centerlink," said Eva.
The Bimtek also discussed the material "Guidance and Supervision of LKS" by the Head of Sub-Directorate of LKS, Directorate of Individual, Family and Community Institutional Social Empowerment of Social Empowerment Directorate General, Ibnu. "To optimize the fulfillment of individual basic needs and handling social problems, the government needs community-based social welfare services, one of which is through LKS", said Ibnu.
The LKS typology based on characteristics is divided into 4 types, namely type A/independent, type B/developing, type C/growing and type D/embryo. The typology of the LKS is determined by the social agency/service according to its area of authority. The responsibility for registering LKS is within the scope of social empowerment and social rehabilitation.
The management of data collection for Persons with Disabilities in technical assistance was conveyed by the Head of the Information Technology and System Management Division of the Ministry of Social Affairs' Pusdatin, Joko Widiarto. "Based on DTKS as of October 2020, it shows that there are 621, 618 Social Welfare Service Recipients (PPKS) outside the household, 49,624 individual Potential Sources of Social Welfare (PSKS) and 38,845 group/institutional PSKS," said Joko.
DTKS includes data on PPKS and PSKS, as well as recipients of social assistance and empowerment. PPKS and PSKS data under the coordination of the Directorate General of Social Rehabilitation and the Directorate General of Social Empowerment.
"Persons with Disabilities are one of the PPKS criteria that have been included in the DTKS system. The data includes data on Persons with Disabilities living in the household and LKS/Center/Office Technical Implementation Unit (UPTD). Types of services for LKS with Disabilities registered in DTKS are in accordance with the category of LKS Services and the variety of disabilities , said Joko.
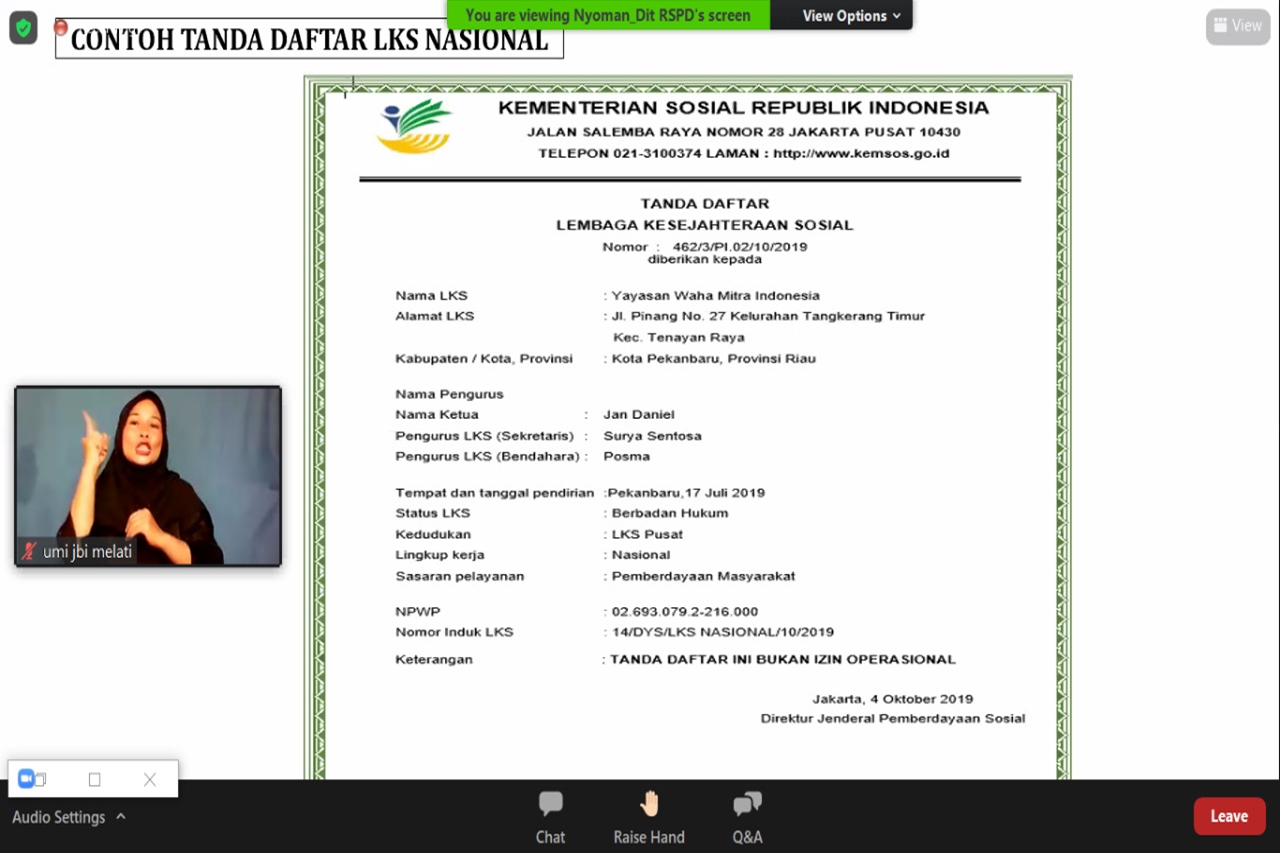
Next, Joko explained the flow of the LKS registration process through the SIKS LKS application for Persons with Disabilities. "First, the LKS registers independently as the Parent LKS to get approval from the district/city social office which is then processed for approval by the PSPKKM Directorate General of Social Empowerment as the Parent LKS," said Joko.
Furthermore, Joko conveyed the second step, LKS registered as an LKS for Services for Persons with Disabilities. Third, LKS completes the Service LKS Profile to get approval from the district/city social office which will be forwarded to the Directorate of Social Rehabilitation of Persons with Disabilities. Fourth, Service LKS registers data for Persons with Disabilities to obtain approval from the district/city social office as the final step for ratifying the Data on Beneficiaries/Persons with Disabilities.
The LKS typology based on characteristics is divided into 4 types, namely type A/independent, type B/developing, type C/growing and type D/embryo. The typology of the LKS is determined by the social agency/service according to its area of authority. The responsibility for registering LKS is within the scope of social empowerment and social rehabilitation.
The management of data collection for Persons with Disabilities in technical assistance was conveyed by the Head of the Information Technology and System Management Division of the Ministry of Social Affairs' Pusdatin, Joko Widiarto. "Based on DTKS as of October 2020, it shows that there are 621, 618 Social Welfare Service Recipients (PPKS) outside the household, 49,624 individual Potential Sources of Social Welfare (PSKS) and 38,845 group/institutional PSKS," said Joko.
DTKS includes data on PPKS and PSKS, as well as recipients of social assistance and empowerment. PPKS and PSKS data under the coordination of the Directorate General of Social Rehabilitation and the Directorate General of Social Empowerment.
"Persons with Disabilities are one of the PPKS criteria that have been included in the DTKS system. The data includes data on Persons with Disabilities living in the household and LKS/Center/Office Technical Implementation Unit (UPTD). Types of services for LKS with Disabilities registered in DTKS are in accordance with the category of LKS Services and the variety of disabilities , said Joko.
Next, Joko explained the flow of the LKS registration process through the SIKS LKS application for Persons with Disabilities. "First, the LKS registers independently as the Parent LKS to get approval from the district/city social office which is then processed for approval by the PSPKKM Directorate General of Social Empowerment as the Parent LKS," said Joko.
Furthermore, Joko conveyed the second step, LKS registered as an LKS for Services for Persons with Disabilities. Third, LKS completes the Service LKS Profile to get approval from the district/city social office which will be forwarded to the Directorate of Social Rehabilitation of Persons with Disabilities. Fourth, Service LKS registers data for Persons with Disabilities to obtain approval from the district/city social office as the final step for ratifying the Data on Beneficiaries/Persons with Disabilities.
The SIKS LKS Bimtek for Persons with Disabilities is a collaboration of the Directorate of Social Rehabilitation of Persons with Disabilities, the Ministry of Social' Affairs' Pusdatin and the Directorate General of Social Empowerment. Participants in the activity consisted of the Provincial/Regency/City Social Office, the Disability Center of the Ministry of Social Affairs, LKSPD, UPTD for Persons with Disabilities, Social Organizations for People with Disabilities, Assistance for Persons with Disabilities (PPD) and Social Welfare Workers for Persons with Disabilities (TKSPD).
 Bahasa
Bahasa
 English
English