JAKARTA (September 26th 2020) - Director of Child Social Rehabilitation of the Ministry of Social Affairs, Kanya Eka Santi explained about "Foster Care of Children (Foster Care)" virtually to prospective foster parents who will take part in the Foster Care program.
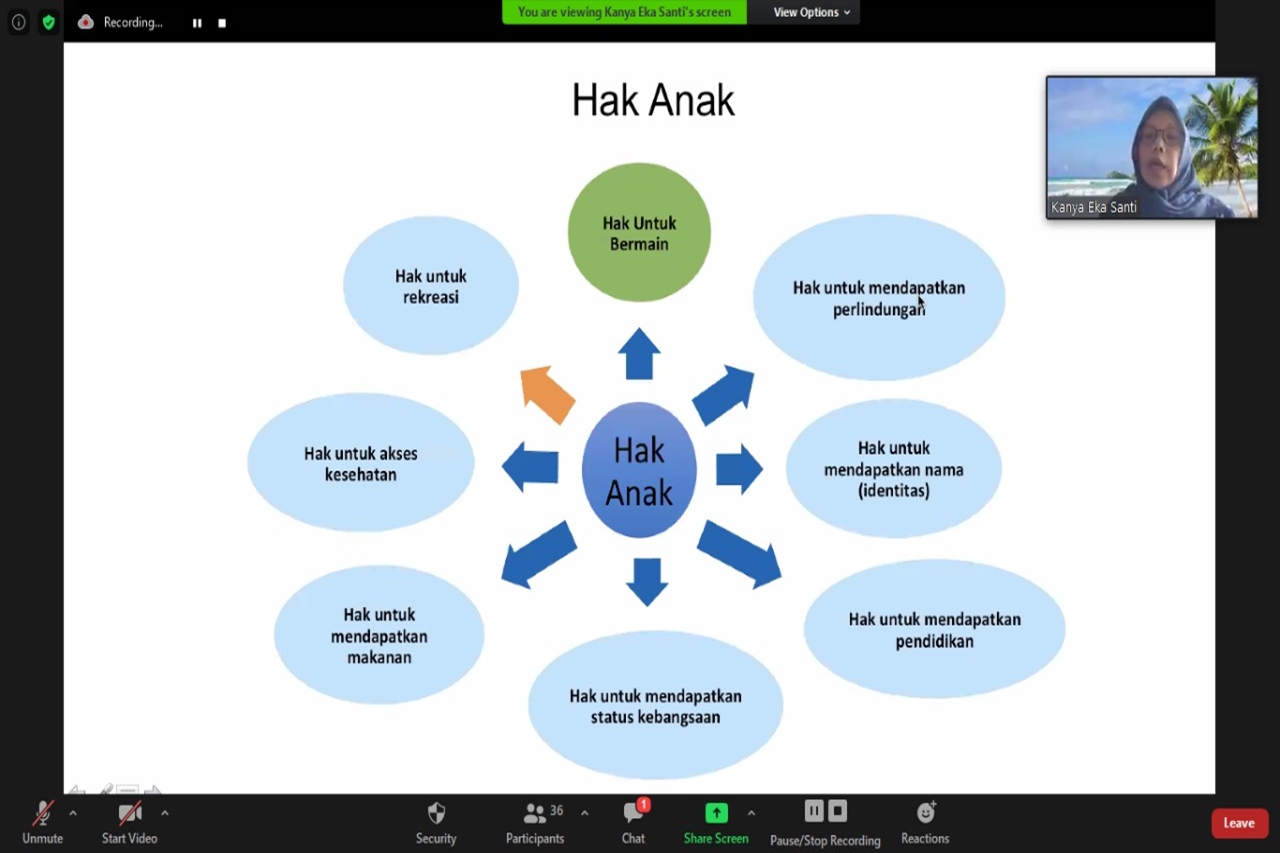
Kanya said that based on the Child Protection Law Number 35 of 2014, a child is someone who is not yet 18 (eighteen) years old, including a child who is still in the womb. "We have to understand the basic rights of children, such as the right to life, the right to grow and develop, the right to protection, and the right to participate," explained Kanya.
Other children's rights are the right to education, protection, health, the right to play, recreation, and the right to get a good name (identity). "The government and society have made efforts to fulfill these children's rights, including through strengthening the family care system and alternative care," said Kanya.
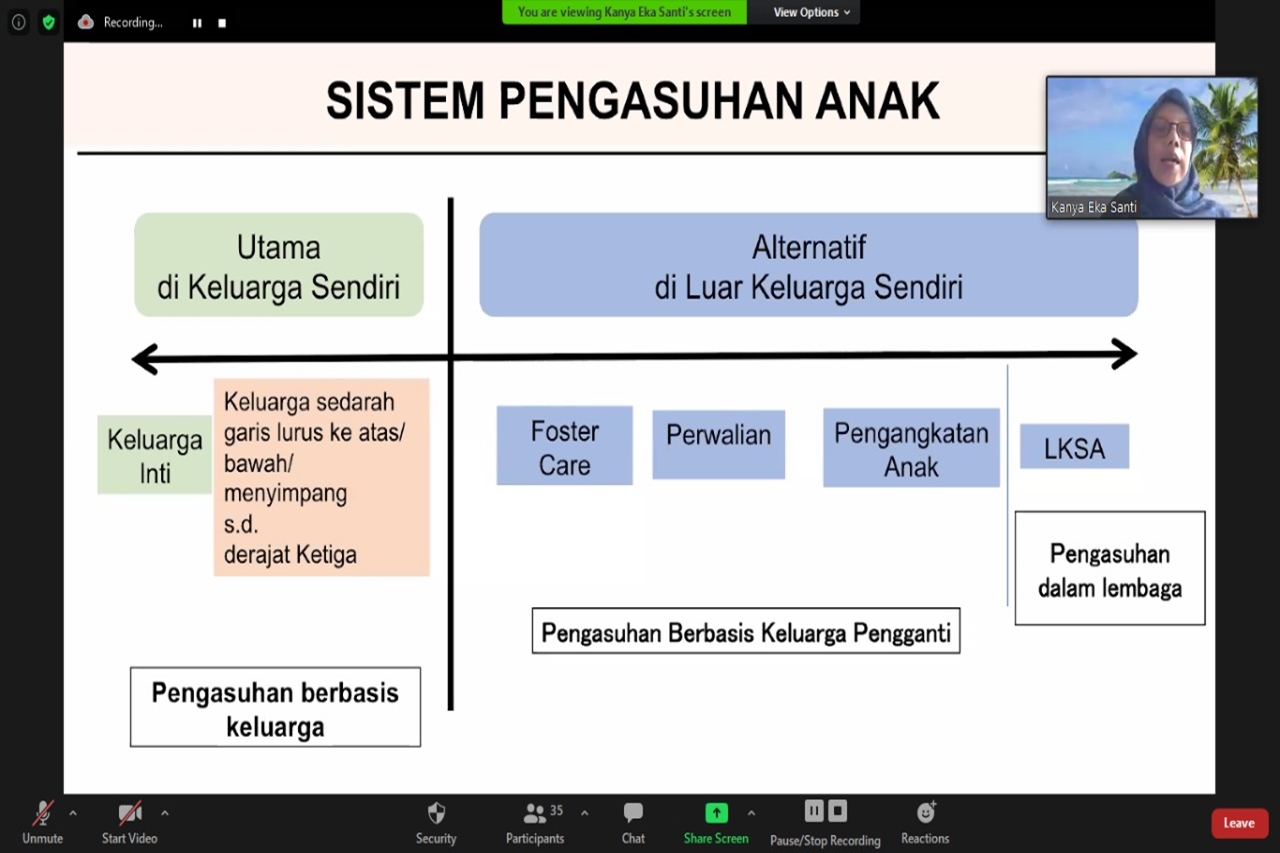
The best parenting system is family-based self-care. However, it does not rule out the possibility of alternative care based on substitute families, namely Foster Care, guardianship and adoption. The last alternative care for children is residential care, which is institutional-based care that is temporary.
Parenting needs to be improved to respond to the current condition of Indonesian children, namely many children left by their parents abroad, children being abandoned by their parents, social and economic exploitation so that children are handed over to other people or even to institutions.
Kanya added, in addition to these conditions, there were also cases of domestic/sexual violence against children, children separated from their parents, kidnapping of children by parents and children abandoned by their parents.
"In response to the child's condition, the Ministry of Social Affairs supports the childcare system in Indonesia with the issuance of Government Regulation Number 44 of 2017 concerning the Implementation of Child Care and has been followed up with a Foster Care trial in collaboration with partner institutions.
The Foster Care procedure is also faster so that children can immediately be with their families. However, this program will be able to run well if the Child Care Institution (LPA) and the provincial/regency/city Social Service are able to carry out their respective duties," said Kanya.
Obligations and responsibilities that must be pursued by foster parents are to nurture, care, educate and protect children according to their dignity and worth, to develop children optimally according to their abilities, talents and interests; preventing child marriage and providing character education and inculcating character values in children.
On that occasion, Kanya also explained about parenting skills. "There are two roles of parents in parenting, namely nurture (providing, carrying out care/nurture) and structure (providing direction, rules, boundaries and values), both of which must be done in a balanced way," concluded Kanya.
If parents only nurture and care without structure or restrictions so that children learn to be responsible then children will be spoiled, not getting appreciation, self-oriented and not learning to do things for themselves.
Conversely, if parents only provide structure without building strong relationships and mutual trust with children, children will feel angry, unloved, ignored, and reluctant to obey rules voluntarily or internalize rules.
Psychologist Abyz Wigati was also present as a parenting resource who gave new enthusiasm for prospective foster parents regarding the best parenting for good parenting children because every child needs a family.
“Every parent who gets the mandate to take care of their children is the person who was chosen as the best person to provide care and education for their children. Every child in our care is a child that God has chosen in our lives," said Abyz Wigati.
The activity was attended by 50 people consisting of prospective foster parents who will participate in the Foster Care program. Program implementation in the assistance of the SOS Children Village institution in Banda Aceh, Lembang, Kupang; LKSA Bud of Hope; PA Darul Ilmi; LKSA Al Marina Gunung Kidul; PA Muhammadiyah Nanggulan Kulon Progo and representatives from the Directorate of Child Social Rehabilitation.
 English
English
 Bahasa
Bahasa